Paul Staniland raises important questions in his review of Philip Roessler’s latest book (highly recommended):
I just finished reading Philip Roessler’s excellent book for my graduate Civil War seminar. Already a fan of his 2005 piece on electoral violence, I learned a lot from the new book and highly recommend it. But, just as when reading major work by Will Reno, Reno and Chris Day, Jeremy Weinstein, Paul Collier, Jeffrey Herbst, and others, I had the reaction that “This looks nothing like the places I study.” At least in the stylized world of African politics presented in these projects (I have no idea if this is accurate), Hobbesian insecurity preys on all in the absence of any real institutions, ethnic balancing and calculation dominates any other form of politics, and regimes are held in place by fluid, shifting alignments with “Big Men” rooted in local power bases.
As a result, we get shambolic and weak central regimes prone to either coups or revolts, and rebels easily bought off by patronage or co-optation. Weinstein highlights the inability of ideological rebels to overcome waves of material resources that eliminate discipline or politics, Roessler’s regimes are simply what Skocpol calls an “arena” for political competition between social actors rather than possessing any institutions or interests autonomous from social forces, and Reno’s civil wars (with the exception of “reform rebels”) are simply a grim game of bargaining over patronage between states and insurgents that are more similar than different.
Is Africa that different?
Roessler, indeed, argues that Africa has a “unique institutional structure” in which external conflicts are rare and internal disorder common. If Africa is indeed unique, it is hard to know how arguments rooted in the African context can travel beyond Africa.
I would argue that there is not a uniquely African civil war story. Weak states everywhere, including in Africa, are gonna weak state.
A more useful analytical delineation is what Staniland suggests:
At minimum, I’m becoming increasingly convinced that research on civil war needs to become at least partially bifurcated into work on its dynamics in very weak states (the representation of African conflicts dominant in the literature, plus Afghanistan and a few others) versus those in medium-capacity states (India, Colombia, Indonesia, Russia, etc) that possess large, centrally controlled conventional an
Think of the Nigerian Civil War between 1967-1970. The Biafra War involved a relatively strong state facing a relatively well-organized and disciplined secessionist army — much in the mold of middle income conflicts. In the same vein, countries like Kenya and Ethiopia have managed to quell rebellions in Mt. Elgon & the south coast, and in the Ogaden, respectively, in ways that would look very familiar to Staniland.
Completely anarchic conflicts involving collapsing states and incoherent hyper-localized rebellions — your stereotypical African conflict, if you will — are a unique historical experience rooted in the states that did really fall apart in the late 1980s to early 1990s (pretty much in the midst of Africa’s continental economic nadir). It is instructive that these states were concentrated in the Mano River region and Central Africa, some of the regions worst affected by the socio-political challenges of Africa’s lost long decade (1980-1995). 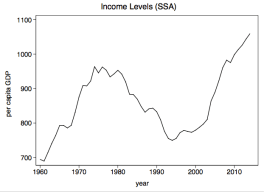
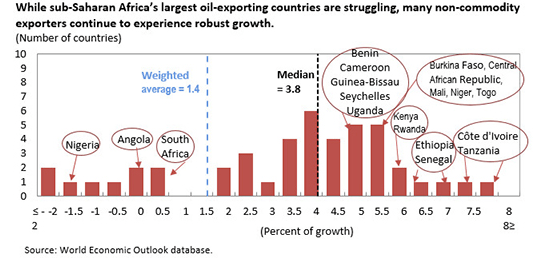
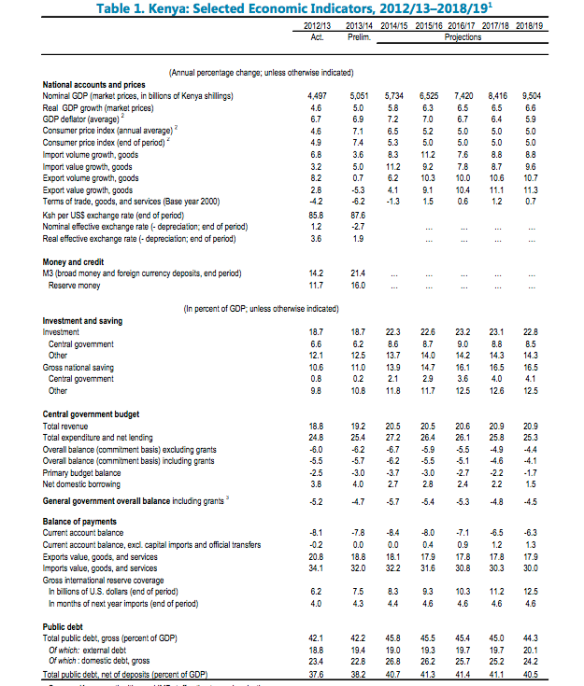
And given recent economic trends in Africa (see image), it is not surprising that conflicts are becoming rarer in Africa (much in line with Fearon and Laitin). I would also expect markedly different kinds of conflicts should they emerge. There is a reason Boko Haram has never posed an existential threat to the Nigerian state, very much in the same way that India’s Maoist rebels are a peripheral matter.
I always remind my students that the Africa they know is more often than not the Africa that existed between 1980 and 1995. We all need to update.
 Take the example of security assistance. If you want to reduce corruption in military procurement, I would suggest that you channel all assistance through the normal appropriation processes in African legislatures. More people will know how much money is going where, thereby increasing the likelihood of greater accountability. The same applies for budget support. Strengthen existing constitutional appropriation processes so that bigger constituencies get to own the aid dollars.
Take the example of security assistance. If you want to reduce corruption in military procurement, I would suggest that you channel all assistance through the normal appropriation processes in African legislatures. More people will know how much money is going where, thereby increasing the likelihood of greater accountability. The same applies for budget support. Strengthen existing constitutional appropriation processes so that bigger constituencies get to own the aid dollars.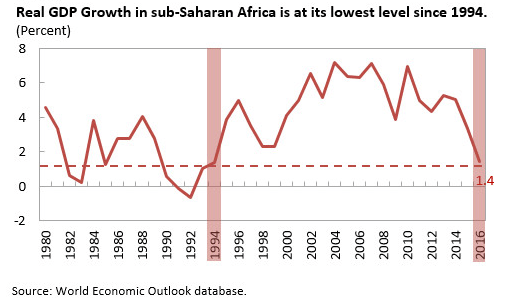

 But no policy is ever built on a blank slate, and surveying the post-Brexit political wreckage, he is now faced with a salvage job that will involve decoupling Britain from numerous EU-led peace and development initiatives and renegotiating dozens of trade deals.
But no policy is ever built on a blank slate, and surveying the post-Brexit political wreckage, he is now faced with a salvage job that will involve decoupling Britain from numerous EU-led peace and development initiatives and renegotiating dozens of trade deals. 
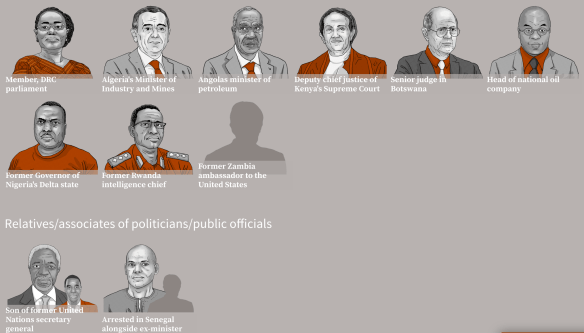
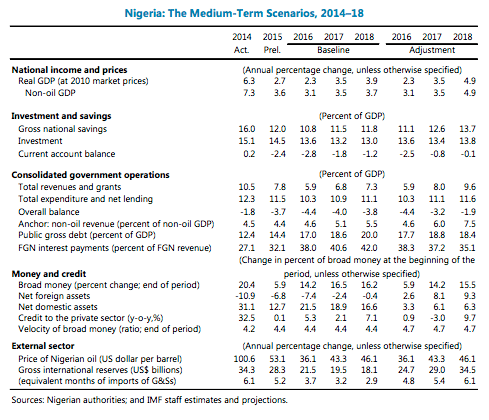
 A federal structure, whose prime objective was to maintain security by curbing regional and ethnic influence, does not foster development. Despite receiving about half the national revenue – a sum of N2.7 trillion in 2014 (US$13.5 billion at current official exchange rate) – state governments fail to provide the services that could materially improve the lives of tens of millions of Nigerians. The 2015 United Nations Human Development Index ranked Nigeria 152nd out of 187 countries. State authorities are not accountable to citizens, state institutions are weak and corruption is endemic. The 774 LGAs – the most proximate form of government for most Nigerians – have all but ceased to function. Furthermore, groups armed by or linked to state governors have been responsible for the most deadly outbreaks of violence of the past decade: ethnic clashes in Plateau state, conflict in the Niger Delta and the Boko Haram insurgency.
A federal structure, whose prime objective was to maintain security by curbing regional and ethnic influence, does not foster development. Despite receiving about half the national revenue – a sum of N2.7 trillion in 2014 (US$13.5 billion at current official exchange rate) – state governments fail to provide the services that could materially improve the lives of tens of millions of Nigerians. The 2015 United Nations Human Development Index ranked Nigeria 152nd out of 187 countries. State authorities are not accountable to citizens, state institutions are weak and corruption is endemic. The 774 LGAs – the most proximate form of government for most Nigerians – have all but ceased to function. Furthermore, groups armed by or linked to state governors have been responsible for the most deadly outbreaks of violence of the past decade: ethnic clashes in Plateau state, conflict in the Niger Delta and the Boko Haram insurgency.