Dear readers, it has been a while since I did a rant and rave post. Here is one to end the long drought. Today we look at a couple of pieces done by Al-Jazeera and the New Yorker.
First The New Yorker.
I love the New Yorker. Everyone does. Unless you are weird. Or do not like their politics.
But the New Yorker should get a better writer than James Verini on the upcoming Kenyan elections. Reporting on the first presidential debate, Verini made several unforgivable errors. I mean, I know it is hard to find information on countries that you may or may not have visited, or have only visited for a few days.
But Kenya is one of the most studied countries on the Continent. You can wikipedia or google your way to a decent article that passes a laugh test. Sadly, Verini’s does not. Here are the necessary corrections to his (original) piece (and certainly not the only ones):
- First of all, there were two moderators, not one. Unless Verini only caught the first half of the debate. I will admit that the second half could have been better. But it wasn’t bad enough to forget that there were two moderators. Julie Gichuru moderated the second half.
- Kenya’s first President Jomo Kenyatta was not a “Mau Mau rebel.” Also, the Mau Mau are popularly known in Kenya as freedom fighters. Dedan Kimathi, a leading light in the independence movement and Mau Mau leader, has a statue in his honor on Kimathi street in downtown Nairobi.
- Kenya’s Prime Minister Raila Odinga is not “a human rights lawyer.” He is “an engineer by profession.” Odinga says so when he introduces himself at the beginning of the debate. What makes Verini think Odinga is a human rights lawyer? (Might be because, as he admits, he was at Njuguna’s – perhaps chasing down goat meat (nyama choma) with Tusker. The New Yorker should institute strict sobriety requirements when sourcing stories, but I digress.)
- Nairobi is not in Central Province. Nairobi is a Province on its own. Kenya has eight provinces (now called regions) – Rift Valley, Eastern, North Eastern, Coast, Western, Central, Nyanza and Nairobi. Nairobi borders Central. But it is not in Central. I swear. You can google it.
- The post-election violence in 2007-08 was not mainly a Kikuyu-Luo affair. Most deaths occurred in the Rift Valley in clashes between Kikuyus and Kalenjins, over land. Police brutality was number two in cause of deaths. Kikuyu-Luo clashes were horrific. But they were not the defining feature of the PEV.
- The 2010 Constitution did not make the position of Prime Minister permanent. It abolished it. You can also google a copy of the Kenyan Constitution. There is a pdf online. I swear. Or you could just read the Wikipedia entry here.
And then Al-Jazeera:
For a news organization that claims to counter the dominance and supposed orientalist biases of CNN International and the BBC with nuanced on-the-ground reporting, this is unforgivable. Here’s is how Peter Greste opens his report on the Kenyan election:
Political science is an imprecise discipline at the best of times. But in Kenya, it feels more akin to witchcraft.
In most established democracies, astute analysts can have a reasonable stab at predicting the outcome of elections. The regular if well-spaced drum-beat of polls gives anyone who cares to look, a decent set of historical data to work with.
It’s usually possible to check the voting patterns of a particular electorate; assess the impact of demographic changes; and with the help of some intelligent opinion polling, have a good understanding of the way a country might swing.
But in Kenya, this election is stacked with so many unknown factors that a witch throwing newt’s eyes into a bubbling cauldron might have as good a chance at predicting the outcome as the political scientists.
Really Mr. Greste, really?
Witchcraft? Why that term? Why not just say that you do not have a grasp of the political reality and so don’t know how the election will turn out? Are you trying to say something about your readers (that they easily resort to witchcraft to explain things they do not comprehend) or Kenya?
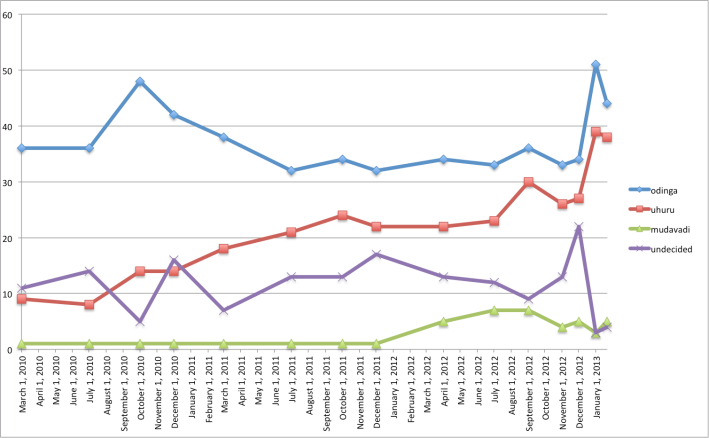
I put it to you that there are three firms that have been polling the Kenyan public on their political preferences since the last election in 2007. These firms accurately predicted the outcome of the messy 2007 election (and pretty much matched the exit polls conducted by UCLA academics) and the 2010 referendum. Kenya has demographic data that politicians make very good use of. For instance, we know the ethnic composition of Nairobi, the most cosmopolitan PROVINCE (hear me, Mr. Verini) in Kenya.
Also, a few political scientists, including yours truly, have done some predictions as to the potential outcomes of the election (see blog posts below).
Why did these two do this?
To me it looks like a bad case of trying to exoticize the Kenyan elections for their audiences – what with the references to witchcraft by Mr. Greste and Mr. Verini’s over-simplification of the election to a Kikuyu-Luo tribal contest.
It is also disrespectful to Kenyans, who they seem to think will not do any fact-checking to correct their sloppiness.