Ipsos just released a poll in which President Uhuru Kenyatta leads Hon. Raila Odinga 48-42% among a representative sample of voting age adults. While this is not a particularly good showing for an incumbent with a few achievements to tout, the poll confirms Kenyatta’s frontrunner status. Furthermore, a 6 percentage point lead combined with his structural advantage in the turnout game mean that if the polls do not narrow any further Kenyatta will likely win in the first round come August 8th. In 2013 most public polls consistently over-estimated Odinga’s support by about 2 percentage points by not accounting for turnout patterns.
A few things other things are worth noting from the Ipsos poll:
- Polls have tightened over the last few months. As Odinga consolidates the opposition, his poll numbers have converged on Kenyatta’s. This is a trend worth watching over the next few weeks.
- The number of undecideds, especially in Coast, Eastern and Western regions, is rather high. This should worry Odinga. Again, Kenyatta has a structural advantage in the turnout game, which means that if Odinga is to have a fighting chance he must ensure that his strongholds register both high turnout rates and give him an even bigger share of their votes than in 2013. That they remain undecided does not bode well for Odinga’s chances. In the table below, Kenyatta’s poll numbers are close to his numbers both in final poll of 2013 and the official election results. Undecideds appear to be voters who sided with Odinga in 2013.
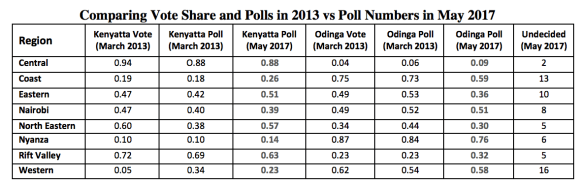
- This poll may be over-estimating Kenyatta’s support in Western region. In 2013 Kenyatta under-performed his poll numbers in Western region by a whole 29 percentage points. And so while his 23% rating in Western region may be a sign that Deputy President William Ruto’s investments are bearing fruit, I would not take these numbers to the bank just yet.
- Odinga has made significant gains in the Rift Valley region since 2013. One way for Odinga to force a runoff (or eke out a squeaker of a first round win) would be to peel off enough voters in from the North Rift. He appears to be doing that. His poll numbers in the region in 2013 were spot on, making his 32% rating in the region believable for now. Recent developments also suggest that he is gaining ground in Narok, Bomet, and parts of Kajiado. That should be a source of concern for the Kenyatta team.
- It is still a turnout game, and Odinga is trailing. The bulk of undecideds — in Coast, Eastern, and Western regions — appear to be likely Odinga supporters. While this may mean that they are likely to break for Odinga in August, it could also mean that they will remain undecided and stay home on election day. Hassan Joho, Kalonzo Musyoka/Charity Ngilu, and Musalia Mudavadi/Moses Wetangula have their work cut out for them.
While a lot may happen between now and August 8th, it is fair to say that Kenyatta is in a strong position. Odinga has several paths to victory, but success along any of those parts is dependent on the NASA coalition running a near-perfect campaign focused on both increasing turnout and running up the score in their strongholds. To this end the lack of enthusiasm in Coast, (lower) Eastern, and Western regions is definitely not a good sign.
The one thing that should worry Kenyatta is Odinga’s apparent gains in the Rift Valley region. If Odinga gains traction in Bomet, it is conceivable that he would also be able to peel off votes in Kericho. It is not that long ago that both Deputy President William Ruto had to camp in Kericho to avoid an embarrassing loss in a by-election. His preferred candidate ended up winning with 66% of the vote. In Bomet, incumbent Governor Isaac Ruto is backing Odinga. And while he will face a tough time swaying voters to Odinga’s camp, it is not far-fetched to imagine that he could bag around 40%. If the same happens in Kericho then two of the Rift Valley’s most important vote baskets will become swing. And Kenyatta would be in serious trouble.
Note: Nearly all the polls this cycle will not take into account any “likely voter models.” I will do my best to guestimate turnout rates based on passed voting patterns and other variables. 2026 out of 5484 contacted agreed to participated in this Ipsos poll.