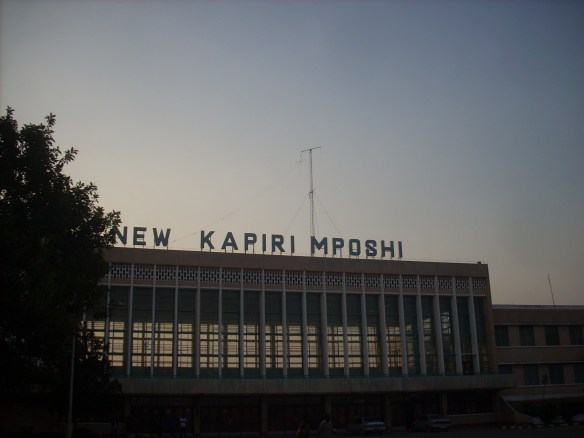
UPDATE: The photos to accompany this post can be found here.
Note: I will post some photos to accompany this post as soon as I get to a place with a faster internet connection. The post is from Friday, September 2nd.
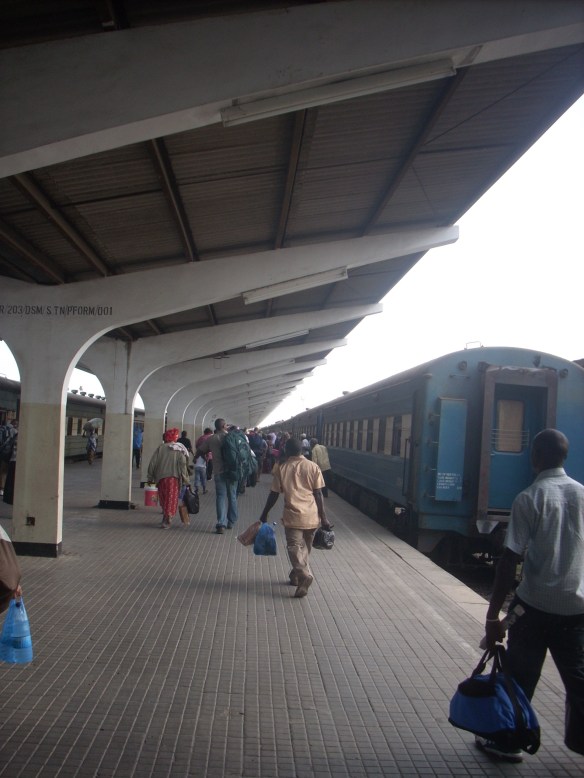
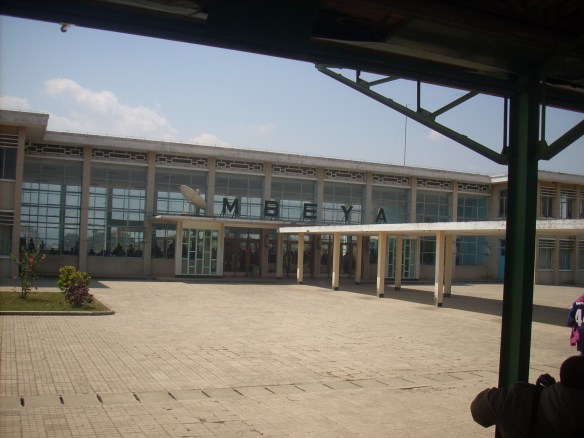
Over the last two days I have been on the TAZARA from Dar es Salaam to Kapiri-Mposhi. The ride lived up to my expectations, despite the many unexplained delays along the way – the longest was a 4-hour wait in Mbeya (where we stopped either to have the engine serviced or wait for the other train from Zambia).
The train was rather old and showed years, if not decades, of disrepair. That said it was clean and livable. The sleeper coaches had two bunk beds each and were swept twice over the whole journey. They had pillows, a bed sheet and a blanket for the beds. The bathrooms were cleaned every few hours by the tireless crew. The train had lounge and restaurant cars. The lounge had a bar with an assortment of beers from Kenya and Tanzania (I had Tusker the whole way). The restaurant had a limited menu of rice or chips and beef or chicken. In the morning they served breakfast of egg, sausage and sliced bread with tea. Food is served both in the restaurant and in the passenger cars.
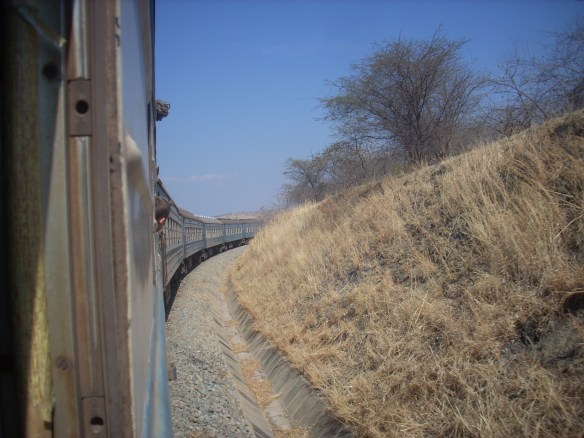
The view along the way was fantastic. The Tanzanian side was sparsely populated while the Zambian side was almost empty. We were unfortunate to pass through Selous Reserve (in Tanzania) during the night so we didn’t see any wild animals on the way. Perhaps the ride from Zambia back to Dar passes through the reserve whilst the sun is still up. But animals aren’t the only natural attraction on the Dar-Kapiri line.
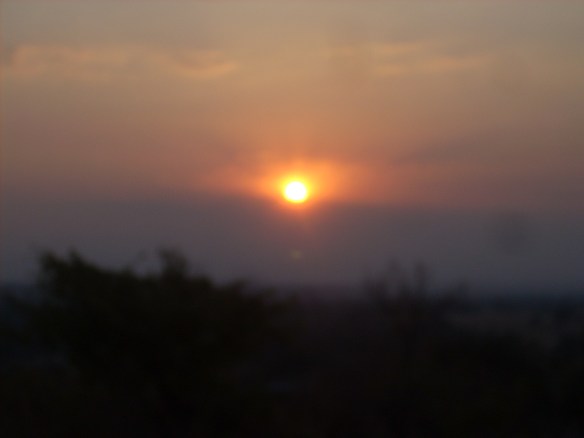
The stunning beauty of the Tanzanian and Zambian countryside more than made up for not having seen any wildlife. The sunrise and sunsets were spectacles to behold. The mountains and rolling hills also provided great views. And then there are the smooth endless rides across the plains of northern Zambia between Mpika and Serenje and again onwards toward Kapiri-Mposhi.
The ride also exposes the endemic poverty in rural Tanzania and Zambia. Quite frankly this was the low-point of the two days.
And it is not just the grass-thatched structures that betrayed their occupier’s meager incomes. At every stop kids with their whole bodies covered in dust would run along the tracks screaming “kopo kopo” (kopo is Swahili for bottle) in a rather bizarre re-enactment of The gods Must be Crazy. People on the train threw empty water bottles, sweets and other items at the kids. Some of them begged for money from the handful of passengers on first and second class cars in the rear of the train.
Day One (Tuesday-Wednesday):
The departure from Dar was delayed.
The previous day I had missed my Akamba bus out of Nairobi in the morning (I overslept and even my older brother’s valiant attempt to get me there on time did not help) and so had to fly to Dar in order to not miss the Tuesday afternoon train. I arrived in Dar on Monday at around 2 PM in the afternoon. Traffic was terrible. I could not find accommodation at the first three places I checked. The fourth place looked rather sketchy – enough to spook even a true Nairobian like me.
So I settled for the pricier Rainbow Hotel close to downtown. The room was very nice – it had a hot shower, air-conditioning and satellite TV. It also had an over-priced restaurant on the second floor that served very well made Indian food.
On arrival in Dar and before going on my hotel hunt I asked the Taxi driver to take me to the train station so I could book my ticket for the next day. The lady at the counter calmly told me that the train was fully booked (first class) until the following Tuesday.
I did not have a week to spend in Dar so I pleaded with her, to no avail. She directed me to the coach class counter with the option of upgrading to first class along the way. I was not wiling to risk sitting in coach for two days. So I bought a first class ticked for the 6th of September (a week later) but decided to try my luck anyway the following day (Tuesday) in case there were any cancellations.
The next day the same taxi driver drove me to TAZARA two hours before the 2 PM reporting time. He then asked one of the luggage handlers if there was any way we could get a ticked before the 2 PM departure time. The man directed us to the office of the stationmaster. It is in there that the lady in charge called the ticket office and asked the person on the other end of the line to sell one Ken Opalo a ticket in first class for the 2 o’clock train. She then took my other ticket. No questions asked.
Because of my desperation to take the TAZARA, I had just been robbed of US $80. Thanks very much TAZARA.
It turns out this is an elaborate scheme: The lady at the counter puts up a sign saying that tickets are sold out until the following weak at which point passengers must see the stationmaster and pay a premium for available tickets. This elaborate scheme has its glitches. For half the trip we had in my compartment a guy who had been sold a ticket in a women only compartment. He slept on the couches in the lounge car the first night.
Departure time was 4.30 PM. In just under two hours dusk was upon us and with it came the darkness that is the African countryside at night. I tried reading but promptly fell asleep. I was however woken up by the loud snoring for the guy on the top bunk and couldn’t go back to sleep for the better part of the long stop at a town called Mrimba.
Wednesday morning I was up by 6.30 AM. I read until the breakfast guy came to the compartment. Thereafter I continued reading until the 4-hour stop at Mbeya where I managed to get off the train and stretch my legs. After Mbeya I went to hang out in the lounge and read a bit more until it was dinner time. By the time the sun set I was so tired that I fell asleep as soon as I finished dinner.
Day Two (Thursday):
Thursday morning I woke up at 5.35 AM. One of the guys in my compartment was getting off at Kasama. He and I had build a sense of camaraderie since leaving Dar es Salaam several hours earlier. He is a globe-trotting businessman and evangelist from Kasama – the Capital of Zambia’s Northern Province. He passionately assured me that Michael Sata will win the Zambian presidential election in three weeks and that the opposition “will not accept anything but victory.” The opposition slogan is “Don’t Kubeba” or don’t say.
The main opposition party is urging its supporters to take all the government money being dished out but not say who they’ll vote for. We helped him offload his many bags and gifts for his family through the window of our compartment. The train then left for Mpika.
Northern Zambia is mostly empty. For hours upon hours we did not see much except trees and the occasional telephone masts and power lines. Human settlements were rare and far in between. The long monotonous ride offered me time to read Railroaded by Stanford’s Richard White. The book provides an excellent account of the political economy of the development of North America’s great transcontinental railroads – I believe that at its inception in the 1970s TAZARA had the same dreams of linking the continent of Africa from coast to coast.
Soon the lunch waiter came knocking. At this point the ware of being in a loud and shaky contraption for almost two whole days was beginning to show. People were quieter. The train was emptier. Everyone was dying to get to Kapiri-Mposhi. I had my last meal on the train – kuku na wali. I then went back to reading in anticipation of the last stop at Kapiri-Mposhi. Even the fact that I still had another leg of the journey to Lusaka (this time by bus) and that I had not yet confirmed my accommodation once I got there did not interfere with my sense of accomplishment. In a few hours I was about to have endured one of the longest train rides in the world.
We arrived at Kapiri-Mposhi at 4.56 PM. The whole journey had take exactly 2 days 1 hour and 26 minutes. The two days without a shower or change of clothes was definitely worth it.
Now I had to endure another one and a half hour bus ride to Lusaka.
As I mentioned above the train schedule was rather unpredictable. But I managed to note down the times on which we arrived at some of the main stations along the way. Here is the schedule for the August 30th train from Dar to Kapiri-Mposhi:
Dar es Salaam 4:30 PM
Nzenga 5:38 PM
Watu 6.00 PM
Kisaki 8.21 PM
Mrimba 11:30 PM
Makambako 8:30 AM
Kangaga 10.08 AM
Rujewa 10:30 AM
Inyala 1:28 PM
Yore 1:53 PM
Mbeya 2:14 PM (we stopped here for 4 hours!!)
Mabrizi 6:33 PM
Idiga 7:05 PM
Tanduma-Nakonde 10:00 PM (Tan-Zam border. We left at 11.15 PM)
Kasama 5.35 AM (Central African Time. The rest of the times below are also CAT)
Mpika 8.45 AM
Kalonje 10.23 AM
Serenje 1.03 PM
Kapiri-Mposhi 4.56 PM
TOTAL TIME: 2 DAYS 1 HOUR 26 MINUTES